

Move 2 units to the left of the origin (as -2 is negative).Solution: Plot the point (-2, 3) as follows: Indicate the quadrant in which it is located. Example 2Įxample 1: Draw a point using the ordered pair (-2, 3). What is the value of y if the value of x is 5? Fill in the blanks with your response in the ordered pair format.Īs a result, the ordered pair for the equation is (5, 25). Ordered pair calculator from equation Example 1 Then, If (x, y) belongs to the relation “is a sister of,” then x is the sister of y.Then, If the relation (4, 2) is “more than,” it signifies that 4 is greater than 2.First, if the expression (2, 4) pertains to the relation “divides,” it signifies that 2 divides 4.A relation is any subset of the cartesian product.Ī relation is, for example, (1, a), (1, b), (3, c). If A = 1, 2, 3 and B = a, b, c, then the cartesian product is A x B = (1, a), (1, b), (1, c), (2, a), (2, b), (2, c), (3, a), (3, b), (3, c), and it is a set created by all ordered pairings (x, y) where x is in A and y is in B. The cartesian product is the collection of all feasible ordered pairings from set A to set B.

They are, however, employed in set theory in a different sense. We’ve seen how ordered pairs are utilised in coordinate geometry to find a point. As illustrated below, (4, -3) and (-3, 4) are positioned at various points on the plane. The order of the elements in an ordered pair is significant, which is why it is called an “ordered” pair. |x| and |y| denote the absolute values of x and y in these stages.īegin at the origin, travel 4 units to the right (since 4 is positive), and then 3 units down (as 3 is negative).Put a dot precisely where you ended in Step 2, and that dot symbolises the ordered pair (x, y).Begin where you left off in Step 1 and travel vertically by |y| units up if y is positive and downward if y is negative.Always begin at the origin and progress horizontally by |x| units to the right if x is positive and left if x is negative.Let us now look at how to graph ordered pairs. We now understand the distinction between an ordered pair’s x- and y-coordinates in coordinate geometry. Atlast, press the “Reset” button to clear the box and input new values.Then, press the “Calculate” button to get the value of y in relation to x.First, fill in the blanks with the equation and the one coordinate of the ordered pair (enter the unknown as x).

To use the calculator, follow the procedures below:
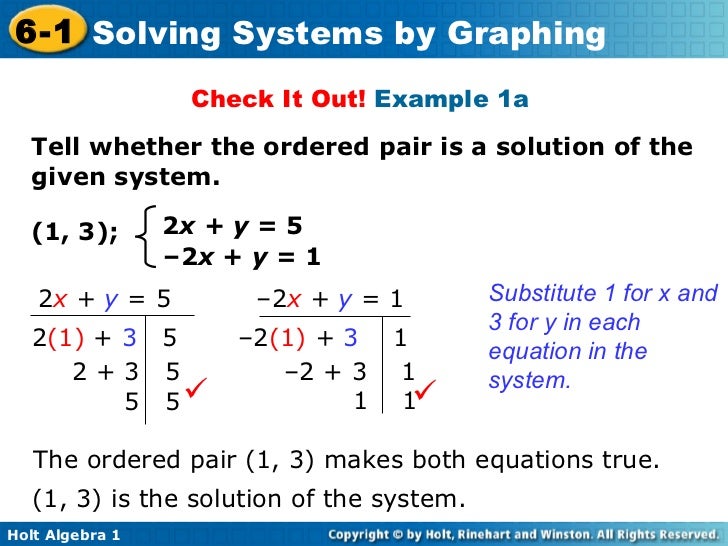
(The unordered pair a, b, on the other hand, equals the unordered pair b, a.) Ordered pair calculator steps The order of the objects in the pair matters: the ordered pair (a, b) differs from the ordered pair (b, a) unless a = b. Sorted pairs A pair of items is an Ordered pair (a, b). Then, both of the variable’s resultant values are represented in the form of (x, y), and this representation is known as an ordered pair. This results in values for both variables that fulfil the specified equation. To get the ordered pair for any equation, substitute any integer or rational number for one of the variables and solve for the remaining variable. Ordered pairs include (2, 5), (a, b), (0, -5), and so on. It indicates that (x, y) may not always be equivalent to (y, x). In an ordered pair, the order of the elements is important. These components have different names depending on the context, and they can be either variables or constants. (x, y) represents an ordered pair, where ‘x’ is the first element and ‘y’ is the second member in the ordered pair. Read Also: Adjacent Angles: Meaning, ExamplesĪn ordered pair is made up of two items separated by a comma and written between the parentheses. They are also used to symbolise components of a relationship. In coordinate geometry, ordered pairs are commonly used to represent a point on a coordinate plane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
